
INTRODUCTION
Cyber security is the practice of defending computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks. It’s also known as information technology security or electronic information security. The term applies in a variety of contexts, from business to mobile computing, and can be divided into a few common categories.
In 2020, the average cost of a data breach was USD 3.86 million globally, and USD 8.64 million in the United States. These costs include the expenses of discovering and responding to the breach, the cost of downtime and lost revenue, and the long-term Reputational damage to a business and its brand. Cyber-criminal’s target customers’ personally identifiable information (PII) – names, addresses, national identification numbers, credit card information – and then sell these records in underground digital marketplaces. But organizations with a comprehensive cyber-security strategy, governed by best practices and automated using advanced analytics, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, can fight cyber-threats more effectively and reduce the life cycle and impact of breaches when they occur.
TYPES OF CYBER SECURITY:
5 main types of cyber security:
1. Critical infrastructure security:
Critical infrastructure security consists of the cyber-physical systems that modern societies rely on. Common examples of critical infrastructure:
- Electricity grid
- Water purification
- Traffic lights
- Shopping centers
- Hospitals
Having the infrastructure of an electricity grid on the internet makes it vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
Organizations with responsibility for any critical infrastructures should perform due diligence to understand the vulnerabilities and protect their business against them. The security and resilience of this critical infrastructure is vital to our society’s safety and well-being.
2. Application security:
You should choose application security as one of the several must-have security measures adopted to protect your systems. Application security uses software and hardware methods to tackle external threats that can arise in the development stage of an application.
Applications are much more accessible over networks, causing the adoption of security measures during the development phase to be an imperative phase of the project.
Types of application security:
- Antivirus programs
- Firewalls
- Encryption programs
These help to ensure that unauthorized access is prevented. Companies can also detect sensitive data assets and protect them through specific application security processes attached to these data sets.
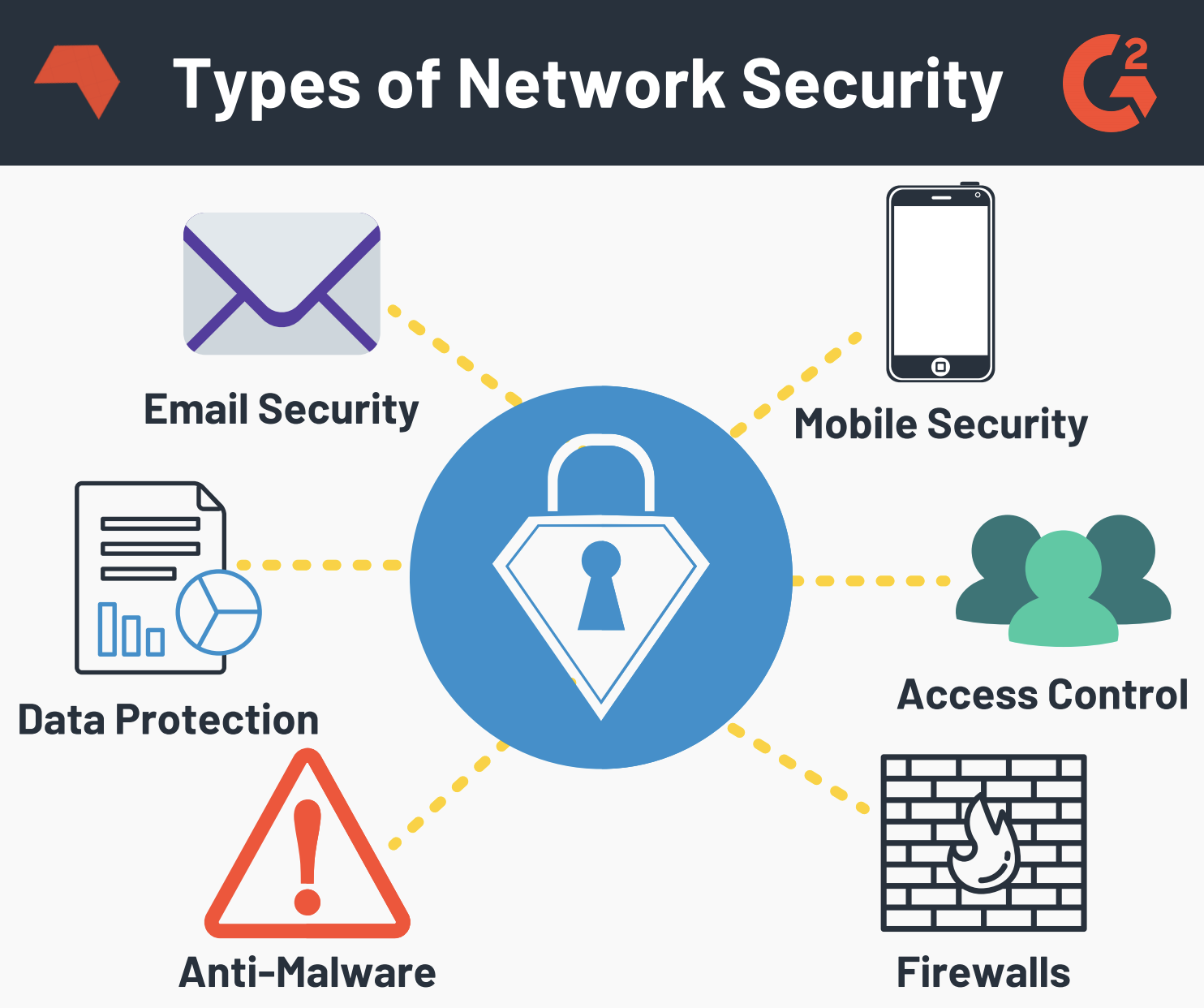
3. Network security:
As cyber security is concerned with outside threats, network security guards against unauthorized intrusion of your internal networks due to malicious intent.
Network security ensures that internal networks are secure by protecting the infrastructure and inhibiting access to it.
To help better manage network security monitoring, security teams are now using machine learning to flag abnormal traffic and alert to threats in real time. Network administrators continue to implement policies and procedures to prevent unauthorized access, modification and exploitation of the network.
Common examples of network security implementation:
- Extra logins
- New passwords
- Application security
- Antivirus programs
- Anti-spyware software
- Encryption
- Firewalls
- Monitored internet access.
4. Cloud security:
Improved cyber security is one of the main reasons why the cloud is taking over.
Cloud security is a software-based security tool that protects and monitors the data in your cloud resources. Cloud providers are constantly creating and implementing new security tools to help enterprise users better secure their data.
The myth flying around cloud computing is that it’s less secure than traditional approaches. People tend to believe that your data is more secure when stored on physical servers and systems you own and control. However, it has been proven through cloud security that control does not mean security and accessibility matters more than physical location of your data.
Cloud computing security is similar to traditional on-premises data centers, only without the time and costs of maintaining huge data facilities, and the risk of security breaches is minimal.
5. Internet of things (IoT) security
IoT refers to a wide variety of critical and non-critical cyber physical systems, like appliances, sensors, televisions, Wi-Fi routers, printers, and security cameras.
According to Bain & Company’s prediction…
- The combined markets of IoT will grow to about $520 billion in 2021.
- More than double the $235 billion spent in 2017.
IoT’s data center, analytics, consumer devices, networks, legacy embedded systems and connectors are the core technology of the IoT market.
IoT devices are frequently sent in a vulnerable state and offer little to no security patching. This poses unique security challenges for all users.
TITLES
CYBER SECURITY: INTRODUCTION.
TYPES OF CYBER SECURITY.
THREATS, TYPES & METHODS USED TO THREATEN CYBER SECURITY.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF CYBER SECURITY.
TOP 2 LATEST CYBER SECURITY TEHNOLOGIES.







CYBER SECURITY
We provide information regarding cyber security and its applications and helps to provide awareness regrading different cyber threats. Thus supporting the local community by providing necessary information.
Get in Touch
Contact Us
7510977535
jayaraj.inmca2025@saintgits.org
